The Vaccine Lifecycle Leads to Vaccine Failure. But Do Vaccines Inevitably Led to Disease Enhancement?
The general public and much of the biomedical community are only vaguely aware of a process that has been recognized in vaccinology since the 1950’s. Clearly, in the end, evolution will find a way.
COVID-19 has compressed the normal life-cycle of a vaccine from decades into a single year. This article provides a review of the factors at play in the inevitable failure of all vaccines that use a fixed antigen source and that are not updated on a routine basis to match the circulating pathogen’s antigenic repertoire and asks an important question: Does vaccination inevitably lead to disease enhancement?
The public, including much of the biomedical community, are only vaguely aware of a process that has been recognized in vaccinology since the 1950’s. Prior to COVID-19, western countries that vaccinate against childhood illnesses were witnessing the occurrence of outbreak of “vaccine-preventable diseases”. Vaccine failure had been acknowledged outright for the vaccination program against pertussis (whooping cough); a large percentage of cases of the measles outbreak at Disneyland involved vaccinated individuals - and worse: measles diagnosis from symptoms from what was recognized in the scientific literature as a “measles-like rash” associated with PCR positive results for the MMR vaccine strain of the measles virus. Completely vaccinated schools - and a military ship - were reporting outbreaks of the mumps (caused by the mumps virus), which was ostensibly preventable via Merck’s MMR vaccine.
Primary vs Secondary Vaccine Failure
As classically defined, Primary Vaccine Failure is the failure of the vaccine to establish immunity in a person in spite of eliciting antibodies. There are three players here: the vaccine, the person, and, of course, the pathogen. The immunocompromised make up a portion of those who remain at risk of infection following vaccination (e.g., liver transplant patients). As early as 2013 it was understood there may be genetic factors to measles vaccine immunity failure. An in 1984 this was published by Levy:
“Little is known about how an intensive measles elimination program changes the overall immune status of the population. A computer model was created to study the effect of the measles elimination program in the United States on the number of susceptibles in the population. The simulation reveals that in the prevaccine era, approximately 10.6% of the population was susceptible to measles, most of whom were children less than 10 years of age. With the institution of the measles immunization program, the proportion of susceptibles in the population fell to 3.1% from 1978 through 1981, but then began to rise by approximately 0.1% per year to reach about 10.9% in the year 2050. The susceptibles at this time were distributed evenly throughout all age groups. The model did not consider the potential effect of waning immunity. The results of this study suggest that measles elimination in the United States has been achieved by an effective immunization program aimed at young susceptibles combined with a highly, naturally immunized adult population. However, despite short-term success in eliminating the disease, long-range projections demonstrate that the proportion of susceptibles in the year 2050 may be greater than in the prevaccine era. Present vaccine technology and public health policy must be altered to deal with this eventuality.”
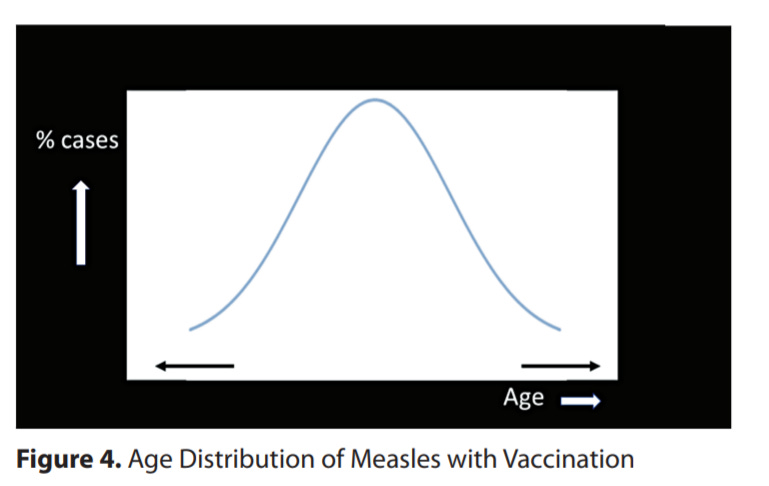
In a nutshell, because the immunity conferred by childhood measles vaccination wears off, the vaccination program shifted the age distribution of measles susceptibility from toddlers to the entire age distribution.
This fact was echoed in the analysis of Heffernan and Keeling in 2009, who published this stunning figure:
The reduction but non-elimination of measles due to mass vaccination was projected to shift some 75 years following the vaccination program to a chaotic oscillation, with some years experiencing massive outbreaks, but distributed across the age groups. We are 59 years into measles mass vaccination. This outcome has nothing to do with anti-vaxxers.
This same problem was described as being due to the “relaxation of permissive constraints” by Andrew Wakefield in 2019. Here is his figure showing the shift of the median age of measles from the young and old to the general population:
Wakefield wrote:
“By 1990, measles incidence was highest for children under 1 year of age, and as was predictable, death rates were highest among these younger children. The unintended consequence of measles vaccination is a loss of the permissive constraint, with a displacement of the age distribution to young children and college-age persons, and consequently increased severity of disease. The “answer,” as it often is in medicine, was to double the dose—to give another shot of the vaccine. In an interview with someone who was part of the National Vaccine Advisory Committee (NVAC), I learned that NVAC had had a recent presentation by an FDA official. The presenter said that we’re seeing a new outbreak of measles, and there’s something different about it. It’s much more severe. Maybe the virus has changed. Maybe under pressure from vaccination the virus has changed. Even though the FDA itself noted this effect, it decided simply that more of the same was the answer.”
This passage anticipates disease enhancement in a highly vaccination population - and part of disease enhancement has to be enhanced transmission, because if the vaccination program leads to an evolutionary shift to other, non-targeted population, the disease will be far more dangerous if waning immunity is accompanied by an inexact immune response to the measles antigens.
Part of the problem is the inexact ability to predict the outcome of evolution - and this leads to a massive underappreciation of factors like original antigenic sin, antigenic drift and vaccine selection. If these factors were given the spotlight as ultimate, root causes, regulatory bodies and the medical community could become far more enlightened on the real issues at hand driving the expansion of vaccine preventable diseases.
Original Antigenic Sin
Those who are infected with pathogens for which the vaccine is an insufficient match make up another portion of those who remain at risk of infection. This is known as original antigenic sin, and has been known to immunology since the 1950’s.
Original antigenic sin is the loss of the ability of the immune response to mount as an effective reaction to newer antigens compared to the reaction to the original antigen source due to the immune system becoming entrained on the original, perhaps extinct antigen source.
In the biomedical literature, it is nearly universal to blame the failure of a vaccine on the patient’s immune system, citing risk factors and conditions that leave them immunocompromised. When it comes to measles, however, at least the US, the occurrence of vaccine failure has been treated almost like starting a lawn mower - clinical re-vaccinate a person who does not produce titers, as if trying again one more time might elicit an immune response. And the unstated assumption, of course, is that mounting “antibodies” is equivalent to demonstrating immunity - untrue for those who mount irrelevant antibodies, for example, against last year’s pathogens.
Or a pathogen isolated in 1960, as is the case in the mumps virus.
More on that in a moment.
Secondary Vaccine Failure
Secondary vaccine failure occurs when antibodies are produced immediately after the vaccination, but the levels fall over time. This is hardly unexpected; antibody levels always fall over time following infection - which is why we have t-cell memory immunity. Secondary vaccine failure is synonymous with waning immunity - but for some reason, discussions usually ignore the role of t-cell immunity. For vaccine immunity to wane, the t-cell memory would also have to become less accurate. Upon follow-up infection, the individual’s antibody production would be less effective at routing out the infection.
Justifications for boosters wipes knowledge of t-cells from the story of immunology, and yet boosting is precisely the strategy adopted by vaccinologists in charge of policy.
Let’s look at these ideas first with the clearest example of vaccine failure: Pertussis.
Pertussis vaccine failure
Originally, the Pertussis vaccination program was designed using whole-cell bacteria (whole, but killed Bordaetella pertussis cells). Reports of developmental disorders including cranial deformities in children born to mothers who were vaccinated during pregnancy and in children vaccinated as infants were sufficient to cause the whole-cell program to be abandoned in favor of acellular pertussis vaccines. If you have vaccine activists, they will incorrectly deny the reports as not relevant because they were not discovered during randomized clinical trials.
Nevertheless, the pertussis vaccination program is a recognized example of vaccine failure; more specifically, a case of vaccination program failure, attributed to multiple factors by Dr. Cherry, including
“decay in antibody over time; a T helper (Th) 1/Th2 versus a Th1, Th17 cellular response; incomplete antigen package; incorrect balance of antigens in the vaccine; linked-epitope suppression; and the occurrence of pertactin-deficient Bordetella pertussis strains.”
Essentially, he’s saying that vaccination fails to elicit a response that mimics the response from infection, and that vaccination with an “incomplete antigen package” could potentially make things worse.
Linked-Epitope Suppression - Worse Than Failed Protection
What if vaccination makes a person more susceptible to infection? This was discussed in 2012 due to a research letter in JAMA (Sheridan et al., 2012).
“The lesser protection provided by DTaP, both as the initial vaccine or full primary course, may be due to linked epitope suppression, when the initial exposure locks in the immune response to certain epitopes and inhibits response to other linked epitopes on subsequent exposures”
Essentially, if you vaccinate using a limited antigen set, and choose the wrong antigen, when the person is exposed to the real pathogen, their immune response may be mistargeted, focused on an antigen that, while present in the pathogen, is not as good as (not as immunogenic as) other antigens present in the full pathogen. A partial immune response will lead to partial and incomplete immunity - which, given enough time, will inevitably lead to vaccine escape.
Such an outcome also characterizes “leaky vaccines”. Some individuals will have a sufficient immune response to ward off infection, but others will not, and that's when evolution works best - variation in the environment and genetic variation in the pathogen leading to partial selection against variation that confers immunity. The reaction? Vaccine selection, and vaccine escape.
Dr. James Cherry has written extensively about the failure of the pertussis vaccination program. In this article, he explains that because of linked-epitope suppression, people who had been primed earlier in their lives as children by DTaP vaccines will be more susceptible to pertussis throughout their lifetimes. He also points out that there is no easy way to decrease this increased lifetime susceptibility. The entire history of what Cherry considers to be a failed vaccination program is reviewed here.
Mumps vaccine failure
By 1998, Japanese researchers had already figured out that secondary vaccine failure was afoot and that avidity testing (which determines the specificity of a person’s antibody production) might be useful. Narita et al. (1998) reported that their results
“showed that secondary mumps vaccine failure occurs not infrequently, even among school age children under condition in which the vaccine coverage is low (i.e., 33% in our study population), and therefore, vaccinees are prone to be exposed to wild-type viruses.”
They concluded that avidity testing would provide information useful for the analysis of mumps virus infections - in other words, mumps from wild-type mumps virus would appear in the vaccinated, and had to be distinguished clinically from side effects of mumps vaccination.
As early as 2006, WebMd was publishing news that the mumps vaccine (MMR) was good, but not perfect - and the CDC came up with a new term: “2-dose vaccine failure”, implying, of course, that a third booster dose would solve the issue. The failure to address the real cause of the failure of mumps vaccines - the fact that the MMR was under contract and given FDA approval as formulated with an ancient mumps virus isolated from a little girl named Jeryl Lynn in 1960.
The alleged efficacy of the MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella) vaccine against strains of mumps virus in 2010 was 18%, according to former Merck employees and whistleblowers who filed suit against Merck on behalf of the US public for providing misleading data to the FDA showing the required >95% efficacy. In a lawsuit filed in 2010, they alleged that they were ordered to spike human serum samples of vaccinees in a study with rabbit antibodies to the mumps virus to fool the FDA into continuing its approval of the MMR vaccine, and Merck’s lucrative monopolistic contract for vaccination against measles, mumps and rubella. If Merck loses or fails to buy a settlement, Merck will be found guilty of defrauding the US public in the process. (See the casework at KellerGrover.com).
By 2014, the public was waking up to the fact that something was not quite right with the mumps vaccination program. Forbes published an article wondering “what’s up with the vaccine?” after an NHL mumps outbreak threatened that lucrative sport. Surprisingly, scientists were frank about the inadequacy of the mumps vaccine, but in the end, the booster solution was the only thing anyone could do.
By 2019, after a mumps outbreak on board the US Navy ship USS Fort McHenry, it became apparent that the mumps program was in serious trouble: all seamen on board had been fully vaccinated. Boosters were sent to help after twenty-five seamen fell ill with viral parotitis (aka “the mumps”), but they evidently did not help. The ship had to stay quarantined at sea for five months.
Antigenic Drift is the change in an epitope via gradual accumulation of mutations. Antigenic Shift involves wholescale loss or gain of epitopes via recombination.
A study published that year in PNAS found that young adults vaccinated as children against mumps have no B-cell immunity, most (80%) who had received two MMR vaccines. The authors described this to “waning immunity”, the authors had measured neutralizing antibody titers to Jeryl Lynn mumps strain and a genotype G mumps virus strain.
Using a full antigen complement can provide a hedge of bets by yielding a diversity of t-cells and a variety of antibodies capable of providing “back up” immunity in individuals or populations. While current literature on mumps vaccine failure addresses antigen drifting, and hints at vaccine selection, it appears to be mute on the question of linked epitope suppression, perhaps because it is thought that because the MMR contains a live, attenuated virus, the full antigen complement is presented. However, mutations, including non-synonymous point mutations, insertions and deletions can dramatically alter the immunogenicity profile of otherwise homologous epitopes. In fact, Genotype G was the most commonly found strain in recent mumps outbreaks, and it was shown in 2018 to have a different immunogenicity profile compared to the Jeryl Lynn strain. Thus, mumps boosters (and all boosters) are predicted to be ineffectual when immunogenicity has changed due to evolution.
This major review from 2020 that questions whether it is time to re-assess the clinical efficacy of mumps vaccines points out that children who have had two doses of the MMR are at increased risk of mumps infection. While the review does not mention vaccine selection, it does mention the limited data on antigenic drift and “lack of cross-neutralization” - which occurs due to antigenic drift.
Both vaccine selection and linked epitope suppression are hypotheses worth exploring to explain the rapidity of waning immunity following mumps boosters.
Measles Vaccine Failure
Failure of measles vaccines is real - with as many as 33% of cases being vaccinated - but outbreaks due to vaccine failure have been met with the same solution - denial and boosters. While it is clear that while this may be a lucrative solution for vaccine manufacturers, the failure to address the root cause of vaccine failure has had a divisive and potentially deadly effect on social harmony.
Measles vaccine failure may be cryptic due to the boosting effect of natural immunity following a milder case of measles among the vaccinated; in such cases, it is logically incorrect to credit the vaccine alone for long-term immunity to the measles virus. Silent boosting, however, remains rather taboo among vaccine activists because with asymptomatic cases comes the prospect of asymptomatic transmission, gutting the justification of mandates for measles vaccination to protect the immunocompromised.
Blaming the Unvaccinated Has Failed. In Fact, It Backfired.
One of their tactics is to shift the focus of questions of vaccine adverse events to the issue of efficacy, and then cast blame for vaccine failure (and failure of the vaccination program) on the unvaccinated. As you’ll see, the clock is running out on MMR efficacy against measles, too.
CDC’s studies show that in COVID-19, the vaccinated can transmit just as easily (if not more easily) that the unvaccinated. Prior to COVID-19, the press loves to blame the unvaccinated, even though, for example, the mumps vaccine has (if you believe recent estimates) 88% efficacy. Here, for example, in 2014, NPR tried to explain how, in spite of reasonably high efficacy, mumps and measles can spread. They tried to blame the unvaccinated, but even in their article, you can see they don’t buy their own argument, citing the case of a
“a young woman in New York caught the measles in 2011 even though she, too, had been vaccinated” who had spread the virus to four others.
All of this was extremely well documented recent history - and then COVID-19 hit. The advent of a so-called “miraculous” mRNA vaccine was touted as having the advantage of being upgradeable - an important attribute given that mRNA viruses evolve faster than DNA viruses and bacteria.
The activist press in the US has stoked the flames of blame in the most atrocious manner possible. In 2015, The Boston Herald published an Editorial that concluded:
“These are the facts: Vaccines don’t cause autism. Measles can kill. And lying to vulnerable people about the health and safety of their children ought to be a hanging offense.”
While most analysts have reacted to the inflammatory “hanging offense”, the author used an interesting phrase choice: “(l)ying to vulnerable people about the health and safety of their children”.
This is something that we see happen routinely, almost every day by vaccine activists who sometimes admit their deeds as if they were self-justified.
Prior to COVID, some news outlets had taken to drawing reckless analogies between the vaccine risk aware (whom they call “anti-vaxxers”) and “terrorists”, and cheap and irresponsible shot in world increasingly trained to react viscerally to anyone labeled a terrorist. It’s worth noting that in every age, the disenfranchised often take the high road, whereas the unenlightened majority often resort to destruction and violence - as if might makes right - and it’s evidently the human condition to forget this massively valuable lesson in objective ethics.
In spite or, or better yet as evidenced by their vitriolic hot air aimed at people who cannot or choose to not vaccinate, vaccine activists have necessarily shifted into the anti-science camp: it is unscientific to ignore or deny science, its predictions, its data, its findings, and its conclusions.
For example, measles vaccine secondary failure was studied by Mitchell et al., who, in 2013, found that unvaccinated children with measles diagnoses were more likely to have more serious symptoms (no mention of Vitamin A amelioration), but, also noteworthy they found that vaccinated individuals with re-infection, who made up nearly half of their case series, had lower IgM responses - that is, their prior vaccination and subsequent infection failed to induce a strong immune response. In that case series, only 54% were age-eligible and unvaccinated. In the multi-state “Disneyland” measles outbreak, 18% of cases had been vaccinated (CDC), and 37.6% turned out to be measles-vaccine virus type “measles-like rash”.
De-emphasis of facts like this and fear mongering masquerading as “main stream press” do nothing to change the facts.
These details should be given due consideration during outbreaks of measles and hype over the fear of serious illness from wild-type measles infection tamed so we can have a return to rational public discourse where decisions about risks and benefits are made based on objective information, not mere propaganda propped up by lawyerly moves to keep critical information on vaccine efficacy under seal, or data manipulation to hide loss of efficacy or lack of safety.
Expect a Public Backlash to Condescending Vaccine Propaganda and Faux Science
Pharma’s campaign to snuff out states rights in the form of religious and philosophical exemptions - the law in 18 states in 2015 - led to a backlash by informed consent and health freedom groups who educated themselves, developed new media outlets and publicized whistleblowers like Dr. William Thompson of the CDC and two whistleblowers at Merck who, like Dr. Thompson, claimed data fudging for key studies. Thompson’s focus was the Destefano et al. study (2004), a key study whose results were to be presented by Dr. Thompson to the National Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Medicine review of science on vaccines and autism. Dr. Thompson had complained to then CDC Director Dr. Julie Gerberding, who arranged to have Thompson put on administrative leave (after being accused of being mentally unwell), and Frank DeStefano presented the results instead. In his presentation, DeStefano claimed to find no evidence of an association between on-time MMR vaccine exposure and autism, and Thompson’s complaint to Gerberding was that the data DID show an association, for two groups: African American males, and so-called idiopathic autism. Destefano left those results out, which were exclude via study design manipulation with the help of Coleen Boyle, which participated in p-hacking: the re-analysis of data using a different set of assumptions to make the association between the exposure (on-time MMR vaccination) and an outcome go away.
The Destefano saga was reviewed in my 2015 book, Cures vs. Profits, and chronicled in the documentary Vaxxed. (See Vaxxed: From Cover-Up to Catastrophe on the IMDB website). The Merck rabbit antibody scandal led to a whistleblower lawsuit from two former Merck employees who allege that Merck falsified data submitted to the FDA on the MMR vaccine efficacy against the mumps. The specific alleged fraud occured via the spiking of human serum samples with rabbit antibodies to mimic a robust immune response in people vaccinated with the MMR vaccine. Merck, of course, has been busy filing for dismissal, and routinely files to keep records of the proceedings sealed.
The Thompson issue was one of safety; theirs was not the only study to find association between autism and vaccination, in spite of the incessant storm of disinformation to the contrary. In contrast, the Merck MMR rabbit antibody spiking allegations deal with vaccine efficacy. In this article, which is likely the final Popular Rationalism article of 2021, I review the evidence of the inevitable end-point of vaccines that are not updated annually to match emerging types/strains/variants.
Vaccine Life Cycle Leading to Vaccine Failure
I have broken the pattern into phases; these are not “official”, nor represented anywhere in the scientific literature (yet) - but they help organize the events that occur inevitably, without fail, in the face of new variation in vaccine-target pathogens. Standard molecular evolutionary theory and population genetics tells us the speed of each phase varies with various factors, including:
the baseline mutation rate (input mutation rate) of the pathogen (high is bad);
the ability of the pathogen to recombine new variation (high is bad);
the degree of isolation of various host (human) populations (high but incomplete is bad);
the number of antigens targeted by a vaccine (low is bad);
the transmission prevention efficacy of the vaccine on the day it is used in a mass vaccination program (low is bad).
Immunology, sociology and psychology tells us that certain other factors also will influence how fast a pathogen will escape a specific vaccine, including:
host features such as the ability to form antibodies (short-term), and B- and T-cell immunity (long-term);
the safety of the vaccine (adverse events will result in vaccine risk awareness and refusal);
the honesty with which vaccination proponents approach adverse events (hiding vaccine adverse events, gas lighting patients, etc. will increase the shock reaction of denied events and result in firm vaccine refusal).
The Phases of Vaccine Failure
In this section, I review the events that occur when pathogens are targeted by vaccines. These are generalized, are not distinct (overlap in time) and the higher-numbered phases are not dependent on the lower-numbered ones.
Phase 0. Perfect Antigen Match - “Release Transmission Efficacy”
When a vaccine is identical to the pathogenic with respect to the amino acid sequence and structure of the vaccine and pathogen antigen(s), efficacy should be maximized. It may not be perfect; that depends on myriad factors listed above.
“Transmission efficacy” is the ability of a vaccine to prevent a new infection leading to disease. This is a function of the level of infection expected in a vaccinated person (bacteremia for bacteria; viremia for viruses). When reading vaccine studies and reports (press releases) it’s important to know the actual definition of efficacy being used. Sometimes companies will initially report on prevention of transmission; then, as real-world studies are conducted, the focus will shift to prevention of death; then to prevention of hospitalization; then to prevention of serious symptoms. That’s when asymptomatic transmission can creep in.
In the end-stage analyses, they may move to using “antibody production” (ideally neutralizing, but read carefully all reports), all the while the public is reading “efficacy” or “effectiveness” as one and the same. They are not. “Efficacy” is an estimate of the ability of a vaccine to do its job (whatever outcome measure is used) in an ideal population; that is, a sample group that is free of pre-existing infection or immunity, one free of comorbid conditions (for the disease), and, often unreported, one free from risk factors for serious adverse events.
With a perfect antigen match, on an idealized population, Transmission Efficacy can look very high. Yet while that is not expected to translate to real-world high effectiveness, long-term large randomized trials including everyone to which the vaccine will be offered are rarely conducted. The incorrect generalization of real-world performance characteristics of a vaccine (in terms of safety and effectiveness) from ideal conditions known to lead to false high efficacy estimates is one of the gravest examples of translational failure seen in biomedical research, and it occurs on a routine basis in vaccine research.
Phase 1. Early Mismatch - Original Antigenic Sin
As mutations accumulate in the laboratory-sourced antigen source, they also occur in the wild-type viral or bacterial lineages. Initially, the slight mismatch between the vaccine type and the wild type will tend to cause a slight decay in vaccine effectiveness, unless the vaccine is updated to match the circulating wild-type pathogen. This would likely fall into the category of Original Antigenic Sin, which was first noticed in influenza strain infections: patients who had flu from the influenza virus in one year often had a second bout of more severe influenza in the second year. This is relatively weakening of the immune response, enough to cause more viremia or bacteremia.
The same problem will, of course, occur over time as vaccine antigens in the lab and in the wild evolve away from each other.
Phase 2. Mid Mismatch - Antigenic Drift/Antigenic Shift
A more dramatic loss of an effective immune response occurs when an antigenic epitope is lost wholescale, which can occur in viruses that recombine (swap parts), as can occur with influenza virus and with beta coronaviruses like SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Such an antigenic shift is a single event, and is not gradual - but the effects of vaccine selection will of course be the same regardless of the source of the variation.
Antigenic drift is an unfortunately specific term for what should really be called antigenic evolution: the substitution of variation via the standard processes of origin of genetic variation via mutation, insertion or deletion (presumably excluding variation that arises by recombination), followed by selection: differential survival and replication of variants that tend to help the vaccine-targeted pathogen escape vaccine immunity.
Regardless of what it is called, evolutionary processes are set in place via the act of mass vaccination that otherwise would not have taken place. Here, too, conditions matter - if bubble vaccination is done at the onset of an outbreak, the opportunity for vaccine escape is minimized. But if vaccination occurs at the height of a pandemic, with leaky vaccines, well… we can sit back and watch a case study in evolution occur, right before our eyes.
Phase 3. Late Mismatch - Vaccine Failure
Given evolutionary transitions away from the vaccine type, pathogens will eventually escape the vaccine to the point where additional vaccination in the population and repeated vaccination (boosting) in individuals will become ineffective public health measures. Routine outbreaks will occur in fully vaccination populations - sometimes even those with 100% vaccination coverage.
When this occurs, pushing for further vaccination via restrictions of rights such as free, prior and fully informed consent, religious and philosophical exemptions will only serve to antagonize an increasingly distrusting public who can see vaccine failure - and vaccine adverse events - with their own eyes. The public messaging that increased vaccine uptake is the best way to shut down an outbreak, epidemic or pandemic will (correctly) be seen as propaganda, and the vaccination event itself will be seen as taking on individual risk with neither personal nor collective benefit.
The palliative promise of less severe symptoms will appeal to some, but that will tend to be based on results from past studies not targeting current pathogen lineages, as we have seen with COVID-19 vaccines targeting extinct SARS-CoV-2 variants in use against more recent variants.
Phase 4. Disease Enhancement (Inevitable?)
The inability of vaccine immune defenses to stop or slow an infection is one thing. If mechanisms exist by which the act of vaccination increases the rate of infection in a person, the vaccine will be seen as a risk factor for more serious disease. This outcome is, of course, utterly disastrous, and the scale of damage will be a function of the extent of vaccination.
In SARS-CoV-1, MERS (Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome) virus and RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) vaccination development attempts, disease enhancement was seen (See SARS-COV-2 VACCINE RECOMMENDED READINGS on jameslyonsweiler.com).
I think it is an open question whether fixed vaccines in a world with pathogen evolution will always necessarily lead to disease enhancement of some type.
There is now, unfortunately, mounting evidence that vaccination of individuals using the Wuhan sequence has fostered vaccine escape, and, per my recent article on the work of Jacques Fantini and his team, fostered disease enhancement since the emergence of the Beta variant very early on in the pandemic.
The simplest way to put this: the problem with vaccines is the vaccines.
Some think (or hope) that Omicron may be a planted live attenuated virus, made more transmissible and far less lethal to help end the pandemic, e.g., my colleague and friend Dr. Jessica Rose:
A note of current interest: The New York Times reported that the four diplomats in which Botswana first detected the Omicron variant came from various countries in Europe, not China, as had been speculated.
If you’re not a paid subscriber, please consider pitching in to keep hard-hitting, uncompromising and information-filled articles like this coming in 2022 and beyond.
Some of the references linked to in the text:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Measles cases and outbreaks. http://www.cdc.gov/measles/cases-outbreaks.html. Updated March 2, 2015. Accessed March 4, 2015.
Cherry JD. Epidemic pertussis and acellular pertussis vaccine failure in the 21st century. Pediatrics. 2015 Jun;135(6):1130-2. doi: 10.1542/peds.2014-4118. Epub 2015 May 4. PMID: 25941310. PUBMED
Narita et al, 1998
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Analysis-of-Mumps-Vaccine-Failure-by-Means-of-for-G-Narita-Matsuzono/3a4c29fa2c3e27eaaf48dd67934f0d08969b87b2
Mitchell P, Turner N, Jennings L, Dong H. Previous vaccination modifies both the clinical disease and immunological features in children with measles. J Prim Health Care. 2013;5(2):93–98.
Sheridan SL, Ware RS, Grimwood K, Lambert SB. Number and order of whole cell pertussis vaccines in infancy and disease protection. JAMA. 2012 Aug 1;308(5):454-6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.6364. Erratum in: JAMA. 2012 Oct 10;308(14):1432. PMID: 22851107.







Really great article with a huge breadth in presenting the full scope of vaccination issues along with its history and vocabulary.
"Vaccines" work exactly as intended. The entire PSYOP is built on Deception. Literally everything is a lie from a 'virus' nobody ever isolated, fake PCR test which can't differentiate between a virus and bacteria to a "safe and Effective" bioweapon..it is effective for sure. Wake up people it's not about a virus. We are The Virus they are trying to eliminate. They've told us the truth years in advance. It is the beginning of the satanic End game. They will not stop. In 1992 and 2012 the entire Corona Pandemic scenario was presented to the public during The Olympics opening rituals The Corona End Game. Addendum https://lionessofjudah.substack.com/p/the-corona-end-game-addendum Corona End Game The Truth Behind The Symbols https://lionessofjudah.substack.com/p/the-corona-end-game