The Next Battle Will Be Over Measles Vaccine Failure. Here is Our Preemptive Strike of Facts, Rationality, and Kindness.
Failure to update the measles vaccine has made it impossible to expect sustained protection in many of the vaccinated. Evolution is real.
This article is designed to arm the public with the specific facts and citations they need for the impending restart of the war on facts and information that will be based on deaths reported to be due to measles. There is a slew of links to my pre-COVID articles at the end; each of those, also is a resource for those of you who will show up and educate the committees and legislators on the facts of measles vaccine failure. It will take a while, but read to the end. I offer a protocol to fight for. There’s a lecture by me on HPV Type Replacement and a quote and a video lecture from Dr. Wakefield. - JLW
Vaccines have stripped the human population of a valuable asset against measles virus infection-related immunity, and we’re going to see larger numbers of cases, hospitalizations, and deaths - in populations that prior to the vaccine program were, well, immune. You need resources to be able to explain this reality. Here they are.
Just prior to COVID-19, the public health machinery was gearing up for another round of war against information as part of their eternal war against bodily autonomy and integrity. Their chosen battlefield was one upon which they had started the war: measles.
Why do I say they “started the war”? I don’t mean to imply that they willfully infected people at Disneyland in 2014. I mean, specifically, that alleged bioethicist Art Caplan had specifically openly declared war on people who rejected vaccines. The Boston Herald had also called sharing information about the risks of vaccines “a hanging offense”:
“These are the facts: Vaccines don’t cause autism. Measles can kill. And lying to vulnerable people about the health and safety of their children ought to be a hanging offense.”
Rhetorical arguments based on something other than facts had started to emerge, too. For example, in 2019, a Dr. Vincent Iannelli had published a criticism of Robert F. Kennedy, Jr.’s analysis of the deaths that had been occurring during a measles outbreak in Samoa. In his critique “Are Deadly New Rogue Strains of Mutating Measles Spreading Like Wildfire?”, Iannelli got a few critical facts wrong. For example, critiquing Kennedy’s analysis which reported (correctly) the number of measles cases that had been determined by PCR testing and sequencing to be vaccine-type cases, Iannelli wrote:
“There were no vaccine strain measles cases in California or anywhere else recently.”
The specific reference for the fact that Kennedy was correct, and that Iannelli was incorrect is available. In 2016, three years before Iannelli’s incorrect claim, Felicia Roy and colleagues reported in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology
“Of the 194 measles virus sequences obtained in the United States in 2015, 73 were identified as vaccine sequences (R. J. McNall, unpublished data). In contrast, only 11 of 542 cases genotyped in the National Reference Center for Measles, Mumps, and Rubella in Germany were associated with the vaccine virus.”
Source:Roy F, Mendoza L, Hiebert J, McNall RJ, Bankamp B, Connolly S, Lüdde A, Friedrich N, Mankertz A, Rota PA, Severini A. Rapid Identification of Measles Virus Vaccine Genotype by Real-Time PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Mar;55(3):735-743. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01879-16. Epub 2016 Nov 16. PMID: 27852670; PMCID: PMC5328441.
These scientists were from the National Microbiology Lab, Public Health Agency of Canada; Division of Viral Disease, CDC, USA, the Robert Koch Institute, Berlin, Germany; Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA, and the University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada.
The fact that Ianelli was incurious about where Mr. Kennedy got his exact numbers on vaccine-type cases of “measles” reveals either a bias or Ianelli was relying on unrevealed knowledge that measles-like rashes had been misdiagnosed as “measles”, and thus his statement could be considered correct even though the “cases” counted as “measles” in public health reporting, and he did not care to educate those who might read his article on the 360-degree view of situational information regarding measles in the US at the time.
His sleight-of-mind tactic is precisely the tactic used by the CDC to paint a different story than the actual clinical situation; the medical records of the patients read “measles”; the accounting is changed at a higher level so semantically, no cases of “measles” attributed to the vaccine-type virus are counted; instead, a new diagnostic category was erected “febrile rash illness”. Here’s Ianelli’s “nothing to see here folks article” - he was evidently unaware of the fact that “cases” reported as “measles” were ID’d as vaccine-related due by Roy et al., not by their attending physicians.
The vaccine industry would like the public to believe that the measles virus in the vaccine is not capable of producing measles disease. But in reality, the vaccine-type is capable of reproducing all of the clinical features of wild-type measles infection, and the virus is known to be present in the feces and urine of vaccinated infants. Jenkins et al., (1999):
“Surveillance and laboratory confirmation of measles will increase in importance as Australia implements enhanced measles control. We describe a 17-month-old child with fever and rash after measles-mumps-rubella vaccination. Detection of vaccine-strain measles virus in his urine by polymerase chain reaction confirmed the diagnosis of a vaccine reaction rather than wild-type measles. We propose that measles virus should be sought and identified as vaccine or wild-type virus when the relationship between vaccination and measles-like illness is uncertain.”
Source:Jenkin GA, Chibo D, Kelly HA, Lynch PA, Catton MG. What is the cause of a rash after measles-mumps-rubella vaccination? Med J Aust. 1999 Aug 16;171(4):194-5. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1999.tb123596.x. PMID: 10494235.
I know of cases of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis in parents who changed their infant’s diaper following MMR vaccination. The clinical course for one friend’s wife was devastating. Their child also developed severe autism following that vaccine; she is now a young adult, institutionalized.
Let’s also keep in mind worldwide, not all measles diagnoses are confirmed via nucleic acid testing.
Another flaw in Ianelli’s logic was to point to the fact that >95% of measles cases did not involve more recently evolved measles types. As a respiratory virus, measles has a seasonality, and newer types require more time than “now” to spread worldwide. In fact, multiple lineages of measles are circulating in the human population, just like in HPV and many other endemic viruses.
Also, in measles, as in all viruses, the most deadly types will die out with their victims. Take, for example, the distant evolutionary branch within measles genotype D4. First described as subgenotype D4.2, the virus can be neutralized by vaccine-induced monoclonal antibodies that target the neutralizing epitope (NE). In fact, subgenotype D4.2 has lost epitopes associated with half of the known vaccine-related antigenic sites.
The information wars started prior to COVID on this topic are important; the vaccine industry will blame the unvaccinated for the emergence of D4.2 and any other measles virus that escapes their limited vaccines. Luckily, the scientific literature already contains the truth. Read, for example, from Gil et al. (2018):
“After several years with a low incidence of measles cases, large outbreaks occurred in Europe between 2010 and 2012 after the introduction of the D4-Enfield lineage at the end of 2007, which replaced the previously circulating D4-Bucharest lineage viruses [1,2]. We have also observed this replacement in Spain, whereby all viruses from samples collected after 2008 belonged to the D4-Enfield lineage, whilst the older ones were of the D4-Bucharest lineage. The reasons for the successful spread of the D4-Enfield lineage MeV in Western Europe [2] are not well understood. The development of major measles outbreaks is related to the presence of susceptible population groups in which the virus can spread easily. However, vaccination coverage in Western Europe and Spain was already high before 2010–2012, when these large outbreaks occurred [3,4]. Among the factors that might have contributed to this widespread MeV dissemination could be the special features of the viruses themselves. Recently, MeV strains with non-standard length M-F NCR sequences, belonging to genotype D4, were discovered in USA in cases imported from Europe and India [12].”
Source: Gil H, Fernández-García A, Mosquera MM, Hübschen JM, Castellanos AM, de Ory F, Masa-Calles J, Echevarría JE. Measles virus genotype D4 strains with non-standard length M-F non-coding region circulated during the major outbreaks of 2011-2012 in Spain. PLoS One. 2018 Jul 16;13(7):e0199975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199975. PMID: 30011283; PMCID: PMC6047782.
Importantly, while online authors such as Ianelli bickered and while the US CDC misled the public away from appreciating the importance of the discrepancy between the clinical diagnoses and the public health counts, the real reason for deaths during the measles outbreak in Samoa included deaths following vaccination with contaminated vaccines; the MMR vaccine must be kept cold, and first-hand witnesses shared with the world the fact that the lack of adequate refrigeration of the vaccines, especially in remote villages, had resulted in the injection of untold thousands of people with vaccines containing fungal and bacterial colonies that occur in MMR vaccines that are not properly stored.
This fact, of course, was determined to be heretical. On the eve of COVID, Edwin Tamasese, the sole on-the-ground eyewitness in Samoa at the time who was smart enough to put the pieces of the puzzle together, and also brave enough and with sufficient resources to reach those at risk, was arrested for warning the public about the iatrogenic illness and death associated with unclean vaccines (See ABC News, Dec 6, 2019 "Samoa arrests anti-vaccine activist as it combats deadly measles outbreak").
Tell Edwin his friend James Lyons-Weiler said hello and sends his kind regards (https://twitter.com/tamaseseedwin).
The MMR Vaccine is, Like mRNA Vaccines, a Leaky Vaccine
Dr. Paul Alexander recently wrote:
“IT'S the VACCINE, stupid!!! BQ.1.1 & BQ.1 (63%) now replaces BA.5 sub-variant (14%) as the new dominant clade; REMEMBER, IT'S the VACCINE & not the virus! once you keep using a non-neutralizing vaccine such as these COVID ineffective ones that do not stop infection, replication, or transmission, then they will place sub-optimal immune pressure on the antigen & select for infectious variants!”
COVID-19 has been a boon to the public that has been paying attention on topics that the vaccine industry might not otherwise care to see widely understood; we have seen type replacement, waning immunity, original antigenic sin, and, of course, vaccine escape. We’ve also seen disease enhancement. The difference has been, compared to measles, this progression from vaccine efficacy to vaccine futility and harm has been compressed to a timeframe in which much of the public could actually notice: they would be immune, they were told. Then, shortly thereafter, they learned they would have to be continuously boosted - a prospect which, as I predict, has been soundly rejected by humanity, thank goodness.
What much of the public does not yet know is that the short lifecycle of vaccine futility in COVID-19 is a recapitulation of the exact same processes that inexorably lead to vaccine failure that have been going on with measles over the last seventy years.
Early on, science had figured out that the Measles, Mumps, and Rubella vaccine failed to provide long-term immunity in around 20% of vaccine recipients. (See Pubmed Search: ‘measles’+"waning immunity"). The response of the vaccine industry was to propose higher vaccination coverage and boosters. The failure of boosting is now showing its face, too.
Lawrence Solomon reported in 2014 that herd immunity against measles is impossible, even with >95% coverage
“When measles failed to be eradicated, public health experts decided that a 70% or 75% vaccination rate would secure herd immunity. When that proved wrong, the magic number rose to 80%, 83%, 85%, and then it became 90%, according to a 2001 Health Services Research report. Later health experts commonly cited 95%.
But that too was insufficient — measles outbreaks occur even when the vaccinated population exceeds 95%, leading some to say a 98% or 99% vaccination rate is needed to protect the remaining 1% or 2% of the herd.
But even that may fall short, since outbreaks occur in fully vaccinated populations.”
Consider, for example, the conclusions of this study of measles virus antibody avidity from 2012:
“Measles and rubella induced high-avidity antibodies and mumps induced low-avidity antibodies after both vaccination and natural infection. Waning of both the concentration as well as the avidity of antibodies might contribute to measles and mumps infections in twice-MMR–vaccinated individuals.”
Source: Kontio, M. S. Jokinen, M. Paunio, H. Peltola, I. Davidkin, Waning Antibody Levels and Avidity: Implications for MMR Vaccine-Induced Protection, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, Volume 206, Issue 10, 15 November 2012, Pages 1542–1548, https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jis568
Their paper, of course, was not the only warning sign. Gregory Poland, an ardent pro-vaccine researcher, published this table showing that prior years’ data showed an unacceptably high rate of “breakthrough” cases of measles.
The title of the paper, “The re-emergence of measles in developed countries: time to develop the next-generation measles vaccines?”, was misleading; measles never went anywhere and was, and is still, endemic to the human species. The “re-emergence” they were referencing is, of course, in reference to cases that occur regardless of vaccination status. Another term for the “re-emergence” in a highly vaccinated population is “vaccine failure”.
Source: Poland GA, Jacobson RM. The re-emergence of measles in developed countries: time to develop the next-generation measles vaccines? Vaccine. 2012 Jan 5;30(2):103-4. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.11.085. PMID: 22196079; PMCID: PMC3905323.
Type Replacement = Antigenic Shift = Vaccine Selection = Emergency of Rare Types
With this high rate of loss of immunity, there is no reason to expect anything other than type replacement - just as is well known in COVID-19, and prior to COVID, had been soundly determined to be happening in human papillomavirus virus due to partial HPV targeting.
Here’s a lecture on that problem from 2021 given in Ohio at the height of the COVID-19 madness.
Vaccine escape has allowed the proliferation of COVID-19 variants. In the precise same manner, vaccine escape by measles types can only be expected to lead to a proliferation of types of measles virus, and this is precisely what has recently occurred. Of course, the vaccine industry wants to blame ‘the antivaxxers’, but this makes no sense: infection via wild-type measles provides lifetime immunity; if anything, people who have natural immunity protect the vaccinated from infections their failing vaccine immunity cannot protect them from.
In HPV, and in measles, rare, more dangerous types are being allowed to proliferate due to the release of competitive exclusion from the more common, more successful, less serious variants (types/strains).
The singularly most brilliant analysis I have ever seen of the problem with vaccination approaches to handling medical issues related to measles due precisely to vaccine escape is the analysis I saw presented, and eventually at my recommendation published, by Dr. Andrew Wakefield.
Dr. Wakefield explained how, before the measles vaccine, the very young were the population most at risk of morbidity and mortality from measles virus infection.
Thankfully, mothers who had measles when they were young, conferred early-life protection to their infants via breastmilk. More recent generations of mothers mostly received “immunity” from the MMR vaccine, which as we know now cost them lifetime immunity, and likely entrained their immunity to extinct measles viruses.
Their daughters, of course, received neither the short-term early-life protection against measles nor long-term immunity from the MMR vaccine. Now, as adults, being vaccinated, they now have failing immunity to measles as well - and little to no ability to pass protection through their breastmilk.
Meanwhile, as the older generation of people with natural immunity is dying off from old age and other causes, Dr. Wakefield explained that there has been and is an ongoing age-distribution shift in the susceptibles - those vulnerable to illness from measles infection.
Something else has been happening as well. The first vaccine dose was found to wear off; in 1989, a study of data from an outbreak in 1985/1986 found that 6 percent of children vaccinated were not immune after one dose, and that 5 percent of children doubly vaccinated failed to “seroconvert” - that is, develop neutralizing antibodies against the measles virus. This was rather shocking at the time; four of 13, or 30% of patients who experienced primary vaccine failure also failed to seroconvert.
Source: Mathias RG, Meekison WG, Arcand TA, Schechter MT. The role of secondary vaccine failures in measles outbreaks. Am J Public Health. 1989 Apr;79(4):475-8. doi: 10.2105/ajph.79.4.475. PMID: 2929807; PMCID: PMC1349980. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2929807/
Abstract:
An outbreak of measles in 1985-86 in a community where measles vaccine trials had been carried out from 1974-76 allowed the assessment of the role of secondary vaccine failures in previously immunized children. A total of 188 children from the vaccine trial were followed. Of these, 175 seroconverted initially while 13 (6 per cent) required re-immunization (primary failure). A total of 13 cases of measles, eight of which were laboratory and/or physician-confirmed, were reported in this cohort. Of these, nine cases occurred in the 175 subjects who had hemagglutination inhibition test (HI) and neutralizing antibody responses following the initial immunization. These nine cases represent secondary vaccine failures. An additional four cases occurred in the 13 subjects with primary vaccine failure. We conclude that secondary vaccine failures occur and that while primary failures account for most cases, secondary vaccine failures contribute to the occurrence of measles cases in an epidemic. A booster dose of measles vaccine may be necessary to reduce susceptibility to a sufficiently low level to allow the goal of measles elimination to be achieved.
These data suggested that the vaccination approach to elimination of measles was potentially unlikely, as no one knew what continuous boosting might do.
The Stolen Valor of The MMR Vaccine and
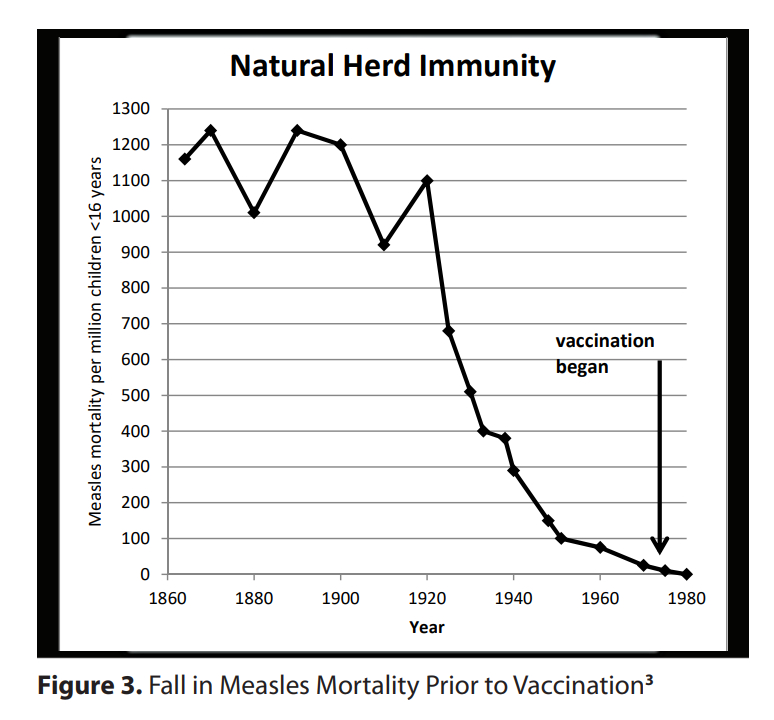
Dr. Wakefield’s publication, “The Sixth Extinction: Vaccine Immunity and Measles Mutants in a Virgin Soil” presents a graph using data from McKeown’s “Modern Rise of Population” which shows that the vaccine industry is guilty of the crime of stolen valor; morbidity due to measles virus infection had decreased for the most part due to factors other than measles infection; whole-population vaccination was a late-comer and deserves little credit.
He also presents a figure that represents the age shift in the diagnosis of measles from ages 3-4 toward the very young and the adult population, including aging vaccinees. The morbidity and mortality from measles infections can be expected to rise in these populations.
Virgin Soil Population Due to Loss of Neutralization of Vaccine Antibodies
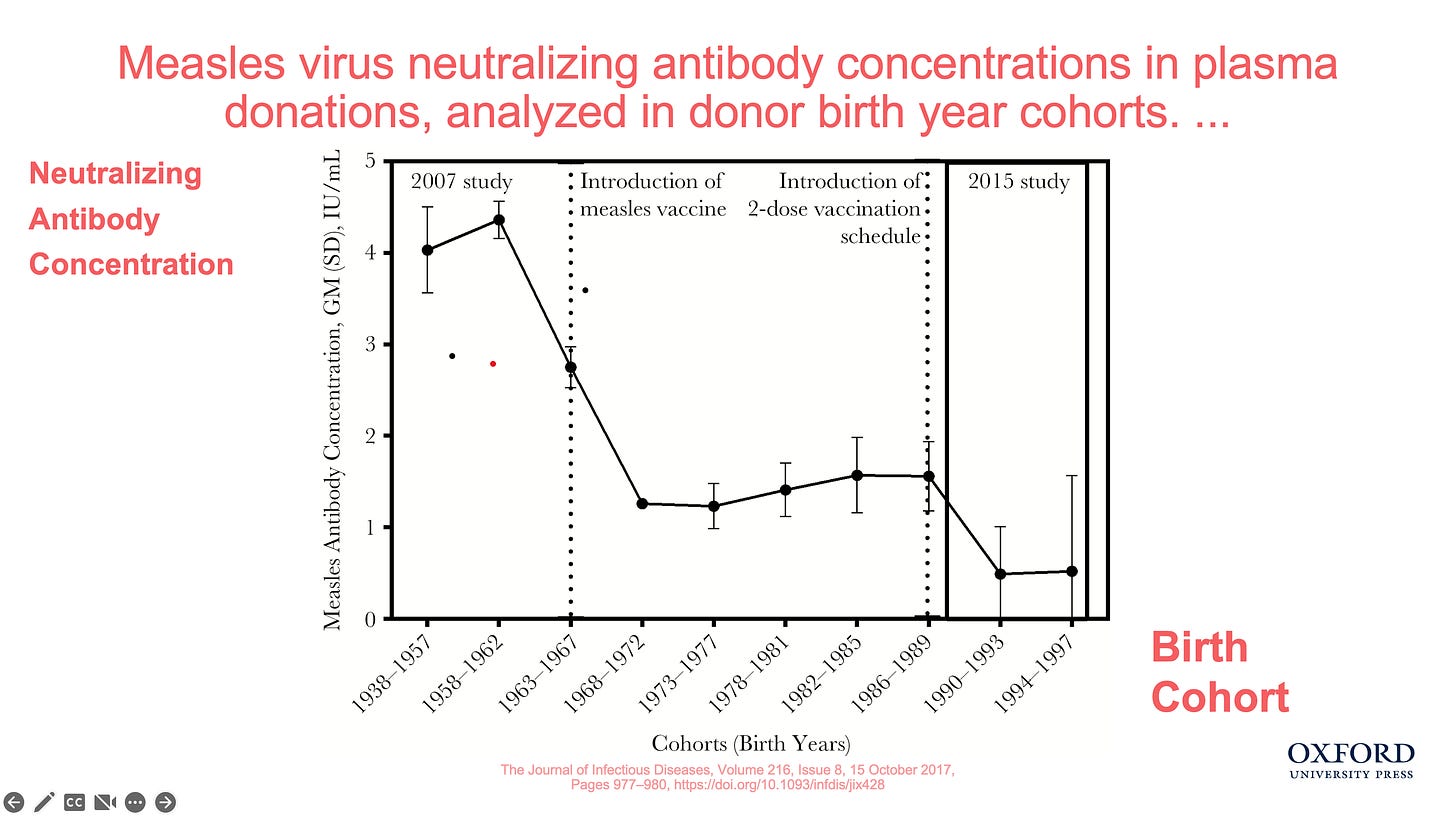
I asked Dr. Wakefield to explain more about this projection. He replied:
“The matter that concerns me greatly is shown in the attached graph. Measles neutralizing antibody titers in healthy blood donor cohorts before measles vaccination (natural infection) and after one and two-dose policies. Neutralizing antibody titers are the Public Health and industry standard of vaccine immunity. This graph really highlights the virgin soil population concern that has been created by vaccination. It also underscores the failure of revaccination to address this issue.”
Modrof, J et al., 2017 Measles Virus Neutralizing Antibodies in Intravenous Immunoglobulins: Is an Increase by Revaccination of Plasma Donors Possible? The Journal of Infectious Diseases, Volume 216, Issue 8, 15 October 2017, Pages 977–980, https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jix428
In a special Guest Lecture in my online course, The Biology of Immunology, Dr. Wakefield explained the entire sad scenario in detail. That video is being made freely available today here:
(Sign up for The Biology of Immunology @ IPAK-EDU - First class in January!)
Dr. Wakefield’s overall analyses were presaged nearly seventy years ago by physician-scientists who noted that, in the then proposed whole-population vaccination approach towards measles, unless the vaccine was updated to match the circulating wild-type measles the world would experience a massive surge in measles cases in - get this - the year 2020. The projected surge in measles cases would be due to the combined effects of waning immunity and vaccine escape - not due to low vaccination.
Massive Numbers of Cases Expected in Highly Vaccinated Populations with Slow Waning Immunity
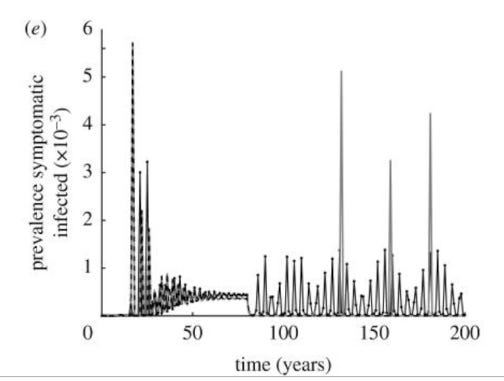
In 2009, Heffernan and Keeling modeled the future of measles case counts following a vaccination program in the face of the dynamic of waning immunity. What they found should inform public health that large outbreaks WILL occur. Here are the patterns they told us to expect under conditions of “high levels of vaccination and slow waning immunity”.
Abstract: For infectious diseases where immunization can offer lifelong protection, a variety of simple models can be used to explain the utility of vaccination as a control method. However, for many diseases, immunity wanes over time and is subsequently enhanced (boosted) by asymptomatic encounters with the infection. The study of this type of epidemiological process requires a model formulation that can capture both the within-host dynamics of the pathogen and immune system as well as the associated population-level transmission dynamics. Here, we parametrize such a model for measles and show how vaccination can have a range of unexpected consequences as it reduces the natural boosting of immunity as well as reducing the number of naive susceptibles. In particular, we show that moderate waning times (40–80 years) and high levels of vaccination (greater than 70%) can induce large-scale oscillations with substantial numbers of symptomatic cases being generated at the peak. In addition, we predict that, after a long disease-free period, the introduction of infection will lead to far larger epidemics than that predicted by standard models. These results have clear implications for the long-term success of any vaccination campaign and highlight the need for a sound understanding of the immunological mechanisms of immunity and vaccination.
Source: Heffernan J.M. and Keeling M.J. 2009 Implications of vaccination and waning immunity Proc. R. Soc. B.2762071–2080 http://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2009.0057
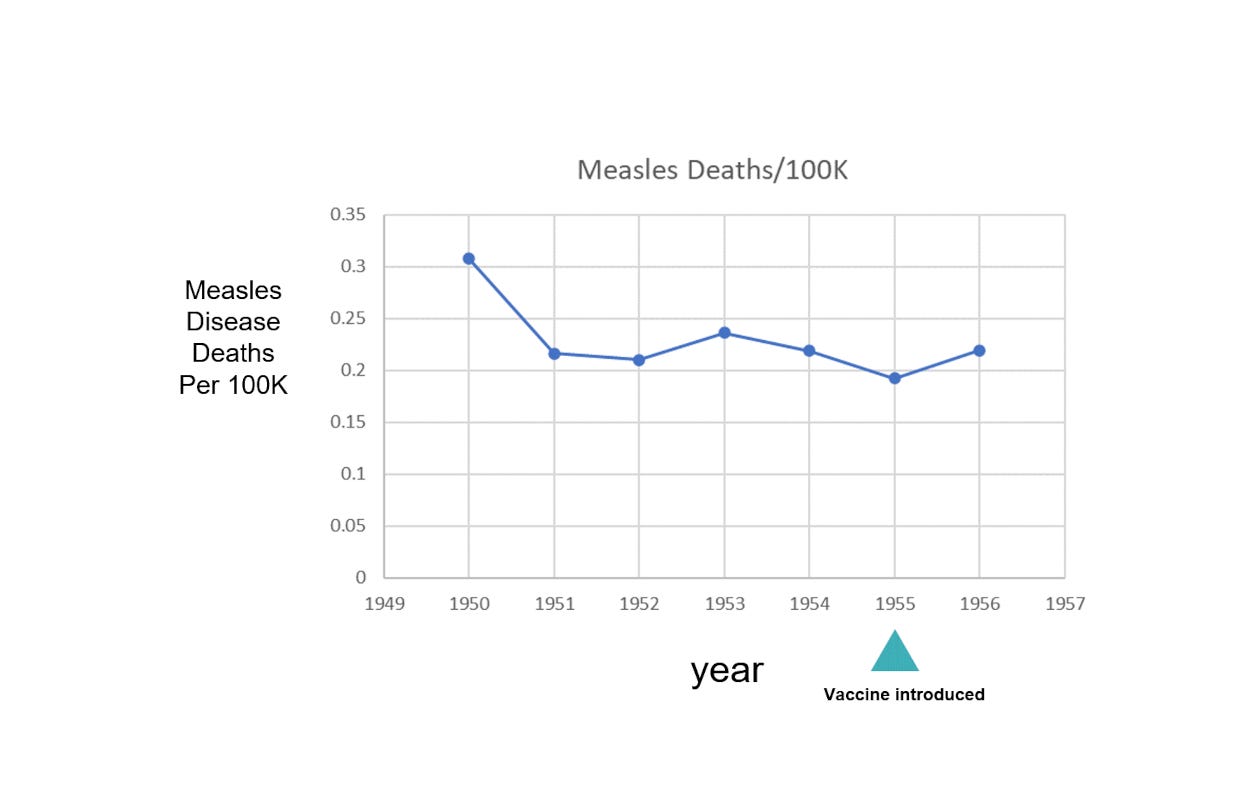
At the time the vaccine was developed, measles deaths in the US occurred at a rate <1 per 100K persons. In the 1960’s, vaccine uptake was never higher than 69%.
Data Sources: https://www.google.com/publicdata/explore?ds=kf7tgg1uo9ude_&met_y=population&idim=country:US&hl=en&dl=en
and
https://web.archive.org/web/20080115193543/https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/downloads/appendices/appdx-full-e.pdf
https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/downloads/appendices/appdx-full-e.pdf
Consider another piece by Poland and colleagues, who point out that herd immunity is not possible via more coverage with a vaccine that has only 94% efficacy:
"...measles eradication is unlikely as population immunity of 96–98% is required to prevent persisting measles endemicity [7,8,27,201]. In a recent study of measles-vaccine efficacy from 1960 to 2010, median efficacy was only 94% [28]. Thus, approaches to eradicating measles will likely require consideration of new measles vaccines and vaccination strategies that overcome the many barriers inherent in the current measles vaccines [6,29–32].”
Source: Haralambieva IH, Ovsyannikova IG, Pankratz VS, Kennedy RB, Jacobson RM, Poland GA. The genetic basis for interindividual immune response variation to measles vaccine: new understanding and new vaccine approaches. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2013 Jan;12(1):57-70. doi: 10.1586/erv.12.134. PMID: 23256739; PMCID: PMC3570049.
“...the proportion of the population possessing only vaccine-induced immunity has increased over time with reduced exposure to wild-type MV infection and there is now evidence of resistance of recent measles virus wild-type isolates to antibody-mediated neutralization in vaccinees. This includes individuals with not only primary but also secondary vaccine failure [7, 8] and is a concern for global MV elimination.”
and
“MV is a serologically monotypic virus and in theory, vaccination should provide life-long protection. However, the proportion of the population possessing only vaccine-induced immunity has increased over time with reduced exposure to wild-type MV infection and there is now evidence of resistance of recent measles virus wild-type isolates to antibody-mediated neutralization in vaccinees. This includes individuals with not only primary but also secondary vaccine failure [7, 8] and is a concern for global MV elimination. It is evident that a better understanding of the molecular basis of MV's escape from neutralizing antibody is required.”
Source: Kweder H, Ainouze M, Cosby SL, Muller CP, Lévy C, Verhoeyen E, Cosset FL, Manet E, Buckland R. Mutations in the H, F, or M Proteins Can Facilitate Resistance of Measles Virus to Neutralizing Human Anti-MV Sera. Adv Virol. 2014;2014:205617. doi: 10.1155/2014/205617. Epub 2014 Feb 4. PMID: 24648840; PMCID: PMC3932291.
From 2011, we see an appreciation for the role of evolution in causes vaccine escape:
“many live-attenuated vaccines exhibit reversion to virulence through back-mutation of attenuating mutations, compensatory mutations elsewhere in the genome, recombination or reassortment, or changes in quasispecies diversity.”
Source: Hanley KA. The double-edged sword: How evolution can make or break a live-attenuated virus vaccine. Evolution (N Y). 2011 Dec;4(4):635-643. doi: 10.1007/s12052-011-0365-y. PMID: 22468165; PMCID: PMC3314307.
There is a large number of additional resources that could be cited, including a few of my own articles that bring forward the balance of the science of measles vaccinology and epidemiology.
Other resources include a massive list at medscienceresearch.com. The measles virus page is still available at archive.org:
http://web.archive.org/web/20201025162327/https://medscienceresearch.com/mmr/
Getting Into Specific Types
The following 19 genotypes have been detected since 1990:
A, B2, B3, C1, C2, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, D10, D11, G2, G3, H1, H2
All vaccine strains (e.g. Moraten, Edmonston-Zagreb) are genotype A.
Since 2018, four genotypes were identified by global surveillance:
B3, D4, D8, H1
Thus, the emergence of B3 and D4 may easily be due to release from competitive exclusion (the Gassian principle in Ecology).
This study nails the fact that things are not what had been expected or hoped for with the measles vaccine program:
Here’s their Abstract:
“The measles virus hemagglutinin (MeV-H) protein is the main target of protective neutralizing antibodies. Using a panel of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) that recognize known major antigenic sites in MeV-H, we identified a D4 genotype variant that escapes neutralization by MAbs targeting the neutralizing epitope (NE) antigenic site. By site-directed mutagenesis, L249P was identified as the critical mutation disrupting the NE in this genotype D4 variant. Forty-two available D4 genotype gene sequences were subsequently analyzed and divided into 2 groups according to the presence or absence of the L249P MeV-H mutation. Further analysis of the MeV-N gene sequences of these 2 groups confirmed that they represent clearly definable, sequence-divergent D4 subgenotypes, which we named subgenotypes D4.1 and D4.2. The subgenotype D4.1 MeVs were isolated predominantly in Kenya and Ethiopia, whereas the MAb-resistant subgenotype D4.2 MeVs were isolated predominantly in France and Great Britain, countries with higher vaccine coverage rates. Interestingly, D4.2 subgenotype viruses showed a trend toward diminished susceptibility to neutralization by human sera pooled from approximately 60 to 80 North American donors. Escape from MAb neutralization may be a powerful epidemiological surveillance tool to monitor the evolution of new MeV subgenotypes.
IMPORTANCE Measles virus is a paradigmatic RNA virus, as the antigenic composition of the vaccination has not needed to be updated since its discovery. The vaccine confers protection by inducing neutralizing antibodies that interfere with the function of the hemagglutinin protein. Viral strains are indistinguishable serologically, although characteristic nucleotide sequences differentiate 24 genotypes. In this work, we describe a distant evolutionary branch within genotype D4. Designated subgenotype D4.2, this virus is distinguishable by neutralization with vaccine-induced monoclonal antibodies that target the neutralizing epitope (NE). The subgenotype D4.2 viruses have a higher predominance in countries with intermediary levels of vaccine coverage. Our studies demonstrate that subgenotype D4.2 lacks epitopes associated with half of the known antigenic sites, which significantly impacts our understanding of measles virus evolution.”
But it’s not as though this was not anticipated. A model of measles vaccine escape conducted in 1984 determined that due to escape, we will eventually see much higher levels than pre-vaccination era - with a high degree of variability expected from year-to-year:
“However, despite short-term success in eliminating the disease, long-range projections demonstrate that the proportion of susceptibles in the year 2050 may be greater than In the prevaccine era.”
Source: Levy DL. The future of measles in highly immunized populations. A modeling approach. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Jul;120(1):39-48. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals. are.a113872. PMID: 6741921.
Why This May Be a Serious Matter: Virgin Soil Population Level-Risk?
Prior to the advent of pushing for ever-increasing vaccine coverage and boosters in the futile aim of eradication, measles vaccination coverage in the US was merely 60-70%.
Serious cases of measles infection were mostly restricted to the very young and elderly. The age-shift distribution of susceptibility is now exposing individuals across the age distribution to potentially serious measles infection outcomes.
The evidence for this is already here; in Ohio, reports of measles infections and hospitalizations such as this one include the remarkably telling statement in a quote in a recent CNN article, which misattributes the emergence of these cases of measles as “driven by ‘lack of vaccination’”:
“I can’t even imagine if your hospital is already chock full and all of a sudden you’ve got to deal with measles, because measles is a really problematic infection-control situation, too. You need negative-pressure rooms, everyone has to wear N95 masks, and it’s incredibly contagious in a hospital,” O’Leary said.
Why, one must ask, would “everyone” have to wear N95 masks, and why would it be “incredibly contagious in a hospital”? In 2022, CDC reports 90.8% MMR vaccine coverage. One presumes this means herd immunity? Let’s see.
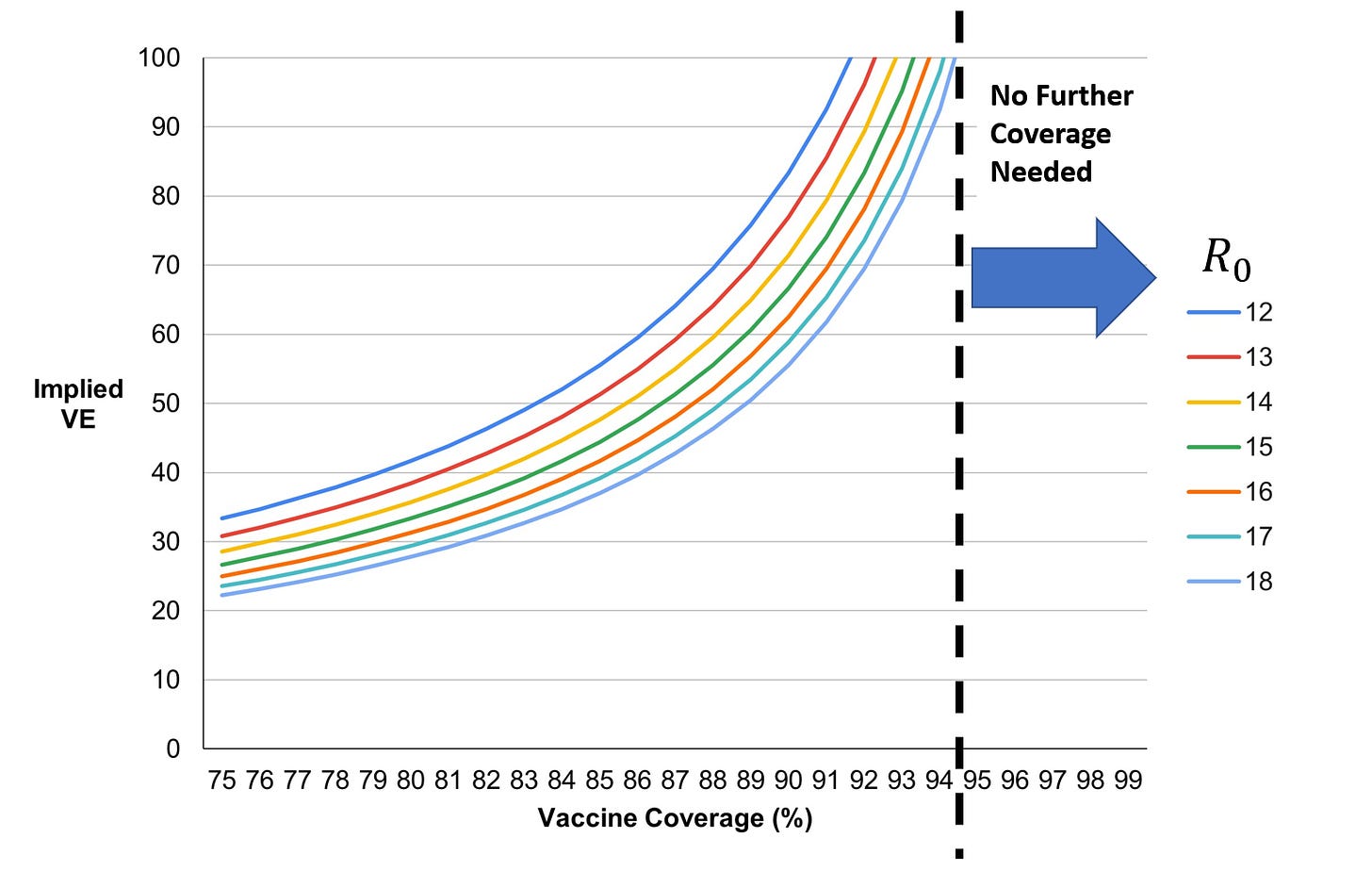
Given Ro = basic reproduction, and VE = Vaccine Efficacy,
The coverage (C) needed to achieve herd immunity is cited as
C = 1-(1/Ro)*(1/VE) (Equation 1)
Measles is reported to have an Ro of 12-18.
When the vaccine industry changed its claim to require vaccine coverage, as outlined, from originally 75% to >95%, their move was an admission of vaccine failure.
Assuming “required coverage for herd immunity” from 75% all the way to 100%, we can use Equation 1 to solve for the implied vaccine efficacy (VE).
VE = 1/(Ro-CRo)
Solving VE for all types of measles
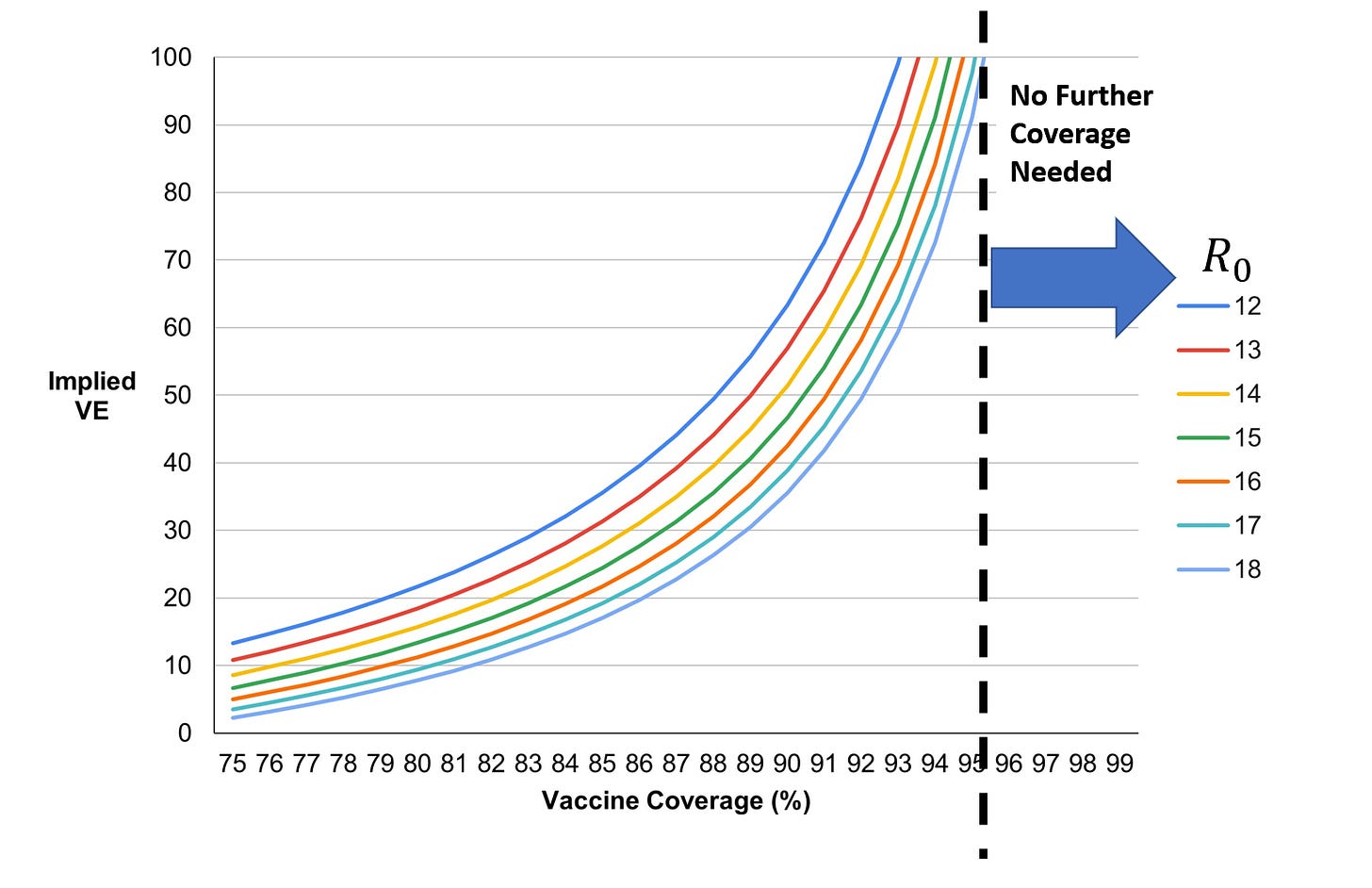
The astute reader will recognize that the implied VE here, of course, is higher than is possible given waning efficacy and vaccine failure. I already mentioned that 20% of people who received the MMR do not have lifetime immunity. Thus, for the adult population, the values of VE have to be adjusted downward, again - due to vaccine failure:
Even with 20% of adults failing to mount an immune response capable of preventing a full-blown measles infection of clinical significance, vaccine coverage (childhood immunization) does not have to be beyond 95%.
In fact, going beyond 95% means tapping into families that avoid vaccines due to their lived experience, places doctors in an untenable position of policing patient choice, all for no net benefit for the population. “For the greater good” fails.
To their credit, the same CNN article that blamed anti-vaxxers for outbreaks also mentioned vitamin A treatment (two high doses of vitamin A reduces the severity of measles). But they failed to mention that many people who were vaccinated as children, upon receiving an exposure to the measles virus during an outbreak, enjoy a free booster without symptoms. This was established years ago by Japanese scientists.
Nasab et al. 2016 found that the B3 measles genotype led to lower neutralizing antibody titers than for the H1, D4 and A genotypes. They concluded that the vaccination program should be updated to address possible vaccine escape.
Nasab, GSF et al., 2016. Comparison of neutralizing antibody titers against outbreak-associated measles genotypes (D4, H1 and B3) in Iran Pathogens and Disease
A team of scientists, publishing in the Lancet in 2018, agreed, and wrote that
“The consequences of the emergence of this new B3 strain on the efficiency of the current vaccine schema and on the goal of eradication, as proposed by Fenner in 1998, are unknown.”
Melenotte C, Zandotti C, Gautret P, Parola P, Raoult D., 'Measles: is a new vaccine approach needed?', Lancet Infect Dis. 2018 Oct;18(10):1060-1061. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30543-7.
When will public health and the vaccine industry admit they have made a massive error? The public should not accept the forthcoming palliation that “MMR vaccine reduces the severity of measles infection in adults”… you read that here first, by the way, but that is precisely what they will do.
Keep your eye on the ball: measles was not a problem in adults until the vaccination program disrupted the natural history of the co-evolutionary processes engaged between the virus and mankind.
What Is To Be Done?
Before I propose food-for-thought solutions, remember: all of the above shows that it’s now vaccine vs. virus, and the vaccine is not evolving, but the virus is. No, I do not support mRNA vaccines for measles - or anything else given the destruction we have seen that has resulted from their use against SARS-CoV-2.
Here are my overall thoughts for public health and the medical community to consider regarding medical and public health considerations of measles:
Public health and the vaccine industry should end their attacks on exemptions. That battle is much ado about nothing: further vaccine coverage will not benefit public health further. Their attacks increase vaccine resistance. Respect choice. NO MEANS NO. Take up our cause, and see what happens. You will be amazed.
Vaccine injury and death denialism must end. Period. This means by everyone. Doctors first. Special Masters in the NVICP next. Witnesses for the defense (HHS) next. CDC. ACIP. VRBAC. Everyone. You have lost. Take up our cause, and see what happens. I am being dead-sober serious.
States without exemptions should put them in place with new legislation. As fast as is humanly possible. There should be bipartisan support for this path forward.
Measles vaccination should not be seen as a panacea, but rather a tool in the toolbox that individual persons and families might want to choose for their children or for themselves.
Schools can respectfully request of parents: if their child is not vaccinated via the MMR vaccines, to please alert the school nurse if their child develops measles or mumps so any immunocompromised child can be protected from the asymptomatic, vaccinated children and teachers who might expose their child to these viruses. They should give assurance that their child’s name will not be made public.
Schools should be required to inform parents of exemption options to vaccines where they exist.
Hospitalists should prescribe two high doses of Vitamin A for all measles infection patients.
People should consider stocking up with a bottle of Vitamin A and keeping it fresh within the expiration date. (Check with your doctor first to see if Vitamin A is right for you).
If, after 7 and 8 are adopted, measles remains a significant clinical concern, then during an outbreak, doctors should consider suggesting that vaccinated adults test for measles memory T-cells - and if they do not have such T-cells, to consider carrying their bottle of Vitamin with them in their purse or bag.
If, after 6 and 7 are adopted, and measles remains a significant clinical concern, as originally prescribed, the measles vaccine should be updated every two years, designed to address local strains whenever possible - and - get this - used in a ring fashion to isolate the virus to a local population. Whole population vaccination has proven to be a failure, as evidenced above. As originally prescribed, respecting, of course, the freedom of choice.
People should be encouraged by their physicians to tend to their overall health. If 20% of adult vaccinees are likely to develop clinical measles infections due to secondary vaccine failure, prophylactic treatment during an outbreak with Vitamin A should be considered.
I am grateful to John Stone, Allie Fujito, Elizabeth Hart, and Dr. Andrew Wakefield for their input on this article. Their name does not imply endorsement of my suggested protocol for the upgrade to medical interventions for measles.
More info on measles below. But first, I heartily recommend this book. Lance has done his homework. It is packed with referenced facts about vaccines. Super-well organized. This will make a great gift for anyone you know who wants the science-based evidence.
Here’s the more info:
FOR HEALTH OFFICIALS AND SCHOOL BOARDS: ASYMPTOMATIC MEASLES INFECTION IS REAL
12.15.2018 jameslyonsweiler Cures 15 comments
There was a time when it was openly recognized that vaccinated individuals could become infected with wild-type measles. These infections are called subclinical infections (aka asymptomatic infections). We don’t talk about that very much anymore. Two days ago I had a conference call with a high-ranking health official at the NYC Health Commission who claimed that it does not happen – specifically, that officials stated that subclinical infections do not occur.
Given that this person is so obviously misinformed, I thought I would provide a literature resource for those who might not realize this reality: vaccinated individuals can, and have always, been known to be able to be infected with wild-type measles virus. Since this is true, the rare non-vaccinated child is not, in a highly vaccinated population, to be the primary source of new transmissions of measles. Instead, the vaccinated individuals with subclinical infections may be driving new infections in schools. It is therefore illogical, and quite unfair, to blame unvaccinated individuals when infected asymptomatic individuals can go to school unabated.
If we are to have public health policies based on science, this science must be given due consideration; otherwise, we would have public health policies based on something other than science. In reality, in highly vaccinated populations, measles can spread from a majority of vaccinated to a minority of unvaccinated people, causing overt disease. In other words, the unvaccinated merely reveal the already circulating measles virus, providing a warning, and any child with a compromised immune system may be exposed even in a fully vaccinated population.
Not all full texts are freely available online, but some are. Here are some relevant examples from the primary scientific literature.
#1. Nonclassic measles infections in an immune population exposed to measles during a college bus trip. Helfand RF https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=9829639
“Mild or asymptomatic measles infections are probably very common among measles-immune persons exposed to measles cases and may be the most common manifestation of measles during outbreaks in highly immune populations.”
#2. Current status of measles in Japan. Nakayama T, Zhou J, Fujino M. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12673398
“Measles infection is considered to provide lifelong immunity after an infection and, thus, live measles vaccines also induce long-term immunity. But long-term immunity is now considered to be an effect of natural boosts via subclinical reinfection. Subclinical infection has been demonstrated by seroconversion, but the isolation or detection of the measles virus genome was rarely demonstrated”…
“Potential impediments to eradication include: (1) a lack of political will in some industrialized countries, (2) transmission among adults, (3) increasing urbanization and population density, (4) HIV epidemics, (5) waning immunity and the possibility of transmission from subclinical cases, and (6) risk of unsafe injection.”
#3. Protective titers of measles neutralizing antibody. Lee MS et al. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11074481
“…only 1 vaccinee with HI titer #31 mIU/ml experienced typical measles symptoms and 13 vaccinees with HI titres #31 mIU/ml experienced subclinical infection.”
#4. Effect of subclinical infection on maintaining immunity against measles in vaccinated children in West Africa. Whittle HC et al. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10023894
“Subclinical measles occurred in 39 (45%) of 86 vaccinated children who were exposed to measles and in four (25%) of 16 unvaccinated children…”
#5. Detection of measles virus genome in lymphocytes from asymptomatic healthy children. Sonoda S, Nakayama T. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11536248
“Serological confirmation of subclinical re-infection was obtained by pre-exposure in household-exposed parents who developed asymptomatic secondary immune responses with a concomitant increase in specific IgG neutralizing test antibodies and haemagglutination inhibition titres…Subclinical infection was confirmed in adulthood.”
“In Japan, measles virus has been circulating and asymptomatic infection has occurred frequently…”
#6. The Clinical Significance of Measles: A Review Walter A. Orenstein Robert T. Perry Neal A. Halsey https://academic.oup.com/jid/article/189/Supplement_1/S4/823958
“People with inapparent subclinical measles virus infections are not known to transmit measles virus to household contacts.”
#7. Detection of measles virus genome in bone-marrow aspirates from adults. Sonoda S, Kitahara M, Nakayama T. http://www.microbiologyresearch.org/docserver/fulltext/jgv/83/10/0832485a.pdf
#8. Waning immunity and subclinical measles infections in England. Glass K, Grenfell BT. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15364464
“A comparison of these cases … shows us that adding subclinical infections to the model also increases the number of clinical cases, as the subclinical infections increase the levels of circulating virus. This feature is more pronounced … because {when) vaccination
levels are higher … subclinical cases make up a greater proportion of the total cases.”
#9. Subclinical measles infection in vaccinated seropositive individuals in arctic Greenland. Pedersen IR https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2815970
“…measles can spread from a majority of vaccinated, to a minority of unvaccinated people, causing overt disease.”
#10. Isolation of measles virus from a naturally-immune, asymptomatically re-infected individual. Vardas E, Kreis S https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10443793
#11. Risk analysis for measles reintroduction post global certification of eradication. Dr Ray Sanders. https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/7._Measles_post_eradication_risk_analysis.pdf
#12. Effect of subclinical infection on maintaining immunity against measles in vaccinated children in West Africa.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(98)02364-2/fulltext
#13. Measles eradication: is it in our future? Orenstein WA, Strebel PM, Papania M, Sutter RW, Bellini WJ, Cochi SL. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1446359/
#14. The Re-Emergence of Measles in Developed Countries: Time to Develop the Next-Generation Measles Vaccines?https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3905323/
#15. Modeling the Impact of Subclinical Measles Transmission in Vaccinated Populations with Waning Immunity Mossong, J et al. https://watermark.silverchair.com/150-11-1238.pdf
“In view of eradication, it is therefore important to investigate whether current vaccines perform well enough to prevent persistence of wild virus in highly or even fully vaccinated populations.”
#16. “Mild or asymptomatic measles infections are probably very common among measles‐immune persons exposed to measles cases, but transmission from asymptomatic cases is likely to be very rare. … However, the potential role of asymptomatic infections in maintaining transmission requires further investigation.”
https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/7._Measles_post_eradication_risk_analysis.pdf
RELATED ARTICLES ON JAMESLYONSWEILER.COM
LIMITS OF KNOWLEDGE ON MEASLES DEATH RATES VS. DEATH RATES FROM MEASLES VACCINES https://jameslyonsweiler.com/2018/08/30/limits-of-knowledge-on-measles-death-rates-vs-death-rates-from-measles-vaccines/
WHAT IS DRIVING PREVENTABLE DISEASE OUTBREAKS? https://jameslyonsweiler.com/2019/02/21/what-is-driving-preventable-disease-outbreaks/
THE PSYCHOSIS OF VACCINE INJURY DENIAL AND HYSTERISIS OF MEASLES MORTALITY https://jameslyonsweiler.com/2019/01/20/the-psychosis-of-vaccine-injury-denial-and-hysterisis-of-measles-mortality/
REASONS GIVEN TO STRIP V@CCINE CHOICE RIGHTS AWAY FALL APART UNDER SCRUTINY https://jameslyonsweiler.com/2019/03/23/reasons-given-to-strip-vccine-choice-rights-away-fall-apart-under-scrutiny/
WANING IMMUNOGENICITY, VACCINE-DRIVEN EVOLUTION AND HYPERIMMUNIZATION: WE CAN NO LONGER DENY THE OBVIOUS https://jameslyonsweiler.com/2019/04/03/waning-immunogenicity-vaccine-driven-evolution-and-hyperimmunization-we-can-no-longer-deny-the-obvious/
MEMO TO HHS ET AL:PERSONAL EXEMPTIONS ARE AN ESSENTIAL SAFETY VALVE ON WHOLE-POPULATION VACCINATION PROGRAMS https://jameslyonsweiler.com/2019/10/24/memo-to-hhs-et-alpersonal-exemptions-are-an-essential-safety-valve-on-whole-population-vaccination-programs/
AN AUTOPSY ON HVIID ET AL. 2019’S MMR/VACCINE SCIENCE-LIKE ACTIVITIES https://jameslyonsweiler.com/2019/03/05/an-autopsy-on-hviid-et-al-2019s-mmr-vaccine-science-like-activities/







"Schools should be required to inform parents of exemption options to vaccines where they exist."
This is a big one. How many parents just go along because they don't know they have any other options? I was one of those parents.
I have been anticipating this upcoming propaganda campaign given the low uptake on all vaccines, so *thank* you for arming us in advance, James! We definitely need to start working proactively instead of reactively.